The stages of project management refer to the different phases that a project goes through from initiation to completion. The specific stages of project management can vary depending on the methodology used, but generally include the following:
Project Initiation: This is the first stage of project management, where the project is conceptualized and defined. The project manager identifies the project goals, objectives, and stakeholders, and creates a project charter.
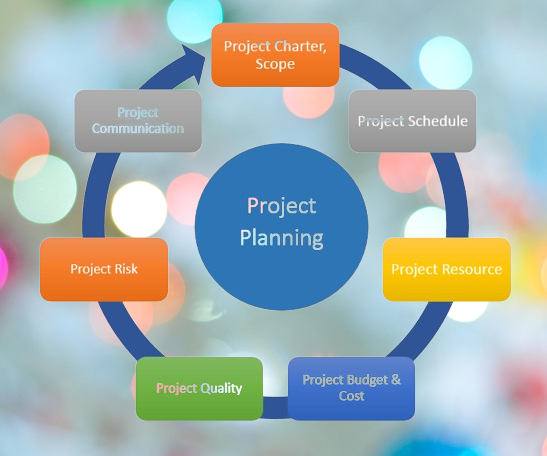
Project Planning: In this stage, the project manager creates a comprehensive project plan that outlines the project scope, schedule, budget, resources, and risk management strategy.
Project Execution: This is the stage where the project plan is put into action, and the project team carries out the project tasks and activities.
Project Monitoring and Control: In this stage, the project manager monitors project progress against the plan, identifies and addresses project issues and risks, and makes adjustments to the project plan as needed to keep the project on track.
Project Closure: This is the final stage of project management, where the project is completed, and the project team obtains approval from stakeholders, finalizes project documentation, and completes any post-project evaluation activities.
These stages are often iterative, meaning that the project manager may need to go back and revise previous stages based on new information or changes to the project scope or objectives. Effective project management requires careful planning, coordination, and communication to ensure that projects are completed successfully on time and within budget.
This article is shared by https://www.itechscripts.com/quality-control/ | A leading resource of inspired clone scripts. It offers hundreds of popular scripts that are used by thousands of small and medium enterprises.